Table of Contents
What is a SPAC?
Imagine a shell company with no actual products or services. Its sole purpose is to raise money through an initial public offering (IPO) and then use those funds to acquire another, private company, taking it public in the process. That’s a SPAC, or Special Purpose Acquisition Company.
Origins and Evolution:
SPACs have been around since the 1990s, but they remained relatively obscure until the late 2010s. A confluence of factors fueled their sudden rise:
- Low interest rates: Made investors more open to riskier investments like SPACs.
- Abundant liquidity: Investors had plenty of cash seeking returns, and SPACs offered an alternative to traditional IPOs.
- Desire for innovation: SPACs promised a faster, more flexible path to public markets, appealing to many fast-growing companies.
The Who’s Who of SPACs:
While anyone can form a SPAC, some prominent figures were involved in the recent boom:
- Chamath Palihapitiya: Dubbed the “SPAC King,” he launched several successful SPACs, including the one that merged with Virgin Galactic.
- Shaquille O’Neal: The basketball legend also partnered with a SPAC sponsor, highlighting the celebrity involvement in the boom.
- Colin Kaepernick: The activist athlete formed a SPAC focused on social justice causes, showcasing the potential for broader societal impact.
SPAC vs IPO
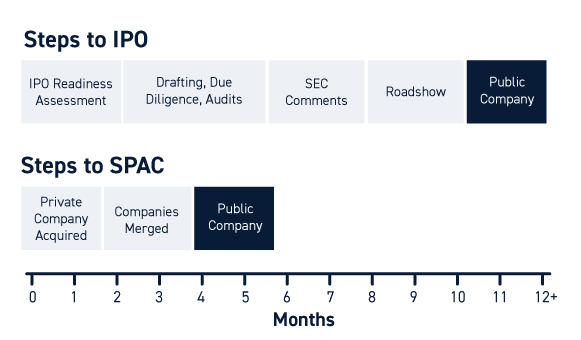
Inshort and the use of SPAC
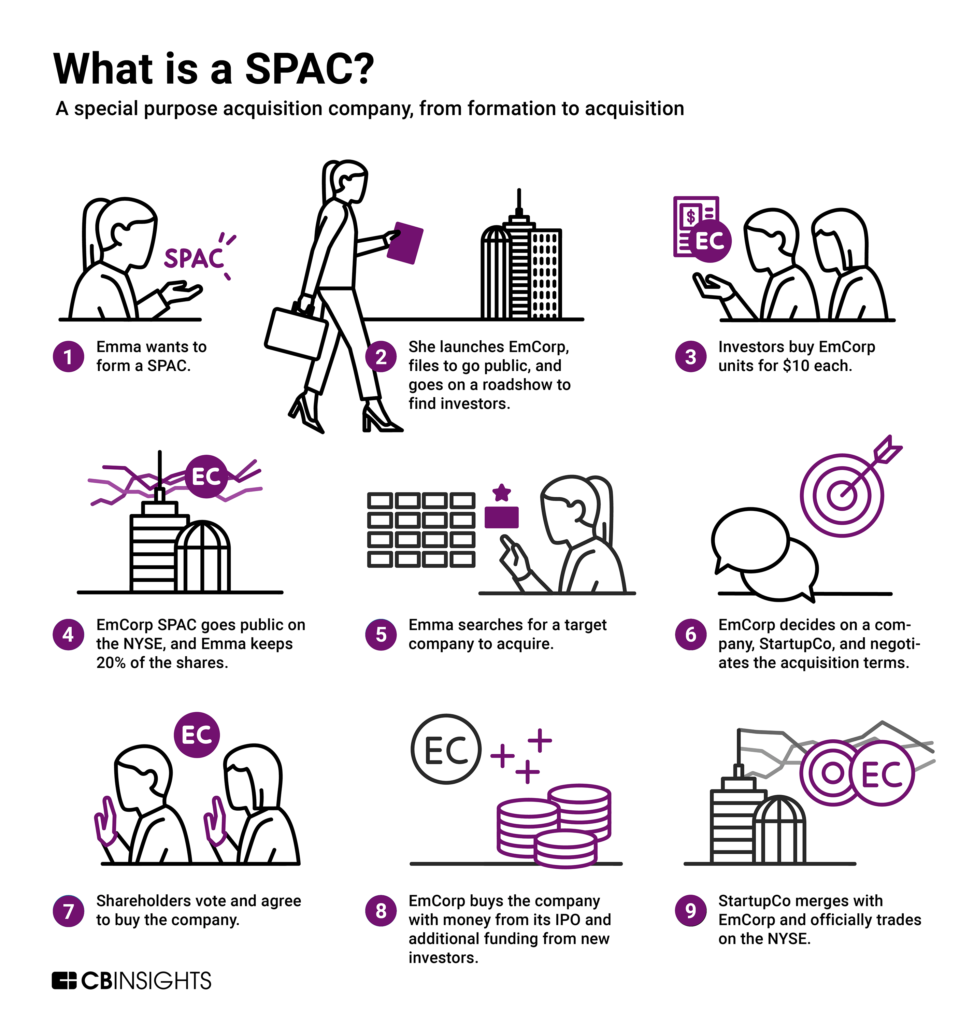
Unveiling the SPAC Utility Belt:
So, what exactly are SPACs used for?
- Faster Public Listings: Compared to traditional IPOs, SPACs can take private companies public in months, not years.
- Flexible Deal Terms: SPACs offer more flexibility in structuring deals, making them attractive to target companies.
- Retail Investor Access: Unlike pre-IPO rounds, SPACs allow regular investors to participate in promising ventures.
Beyond the Hype: A Reality Check:
The SPAC boom wasn’t without its criticisms:
- Inflated Valuations: Many SPAC-backed companies lacked proven track records, yet traded at high valuations, raising concerns about a bubble.
- Due Diligence Concerns: The compressed timeframe for finding target companies raised concerns about rushed deals and potential risks.
- Sponsor Compensation: The significant fees earned by SPAC sponsors, regardless of target company performance, created potential conflicts of interest.
SPACs in the Spotlight: Boom, Bust, and the Uncertain Future:
The SPAC frenzy reached its peak in 2020, but a combination of factors led to a dramatic decline in 2021:
- Poor Performance: Many SPAC-backed companies underperformed, failing to live up to expectations.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Concerns about potential abuses prompted investigations and proposed regulations.
- Market Correction: Rising interest rates and a broader market sell-off dampened investor appetite for risk.
Where Do SPACs Go From Here?
The future of SPACs remains uncertain:
- Regulatory Landscape: New regulations could impact the cost and complexity of SPAC deals.
- Investor Skepticism: Investors are more cautious, demanding stricter governance and clearer terms.
- Niche Applications: SPACs might still find relevance in specific sectors where their flexibility offers advantages.
Beyond the Headlines: Key Players and Case Studies:
- Virgin Galactic: Palihapitiya’s SPAC sent its stock soaring, but concerns about valuation and execution led to a significant fall.
- Latch: This home access solutions company successfully merged with a SPAC, focusing on value creation and responsible use of proceeds.
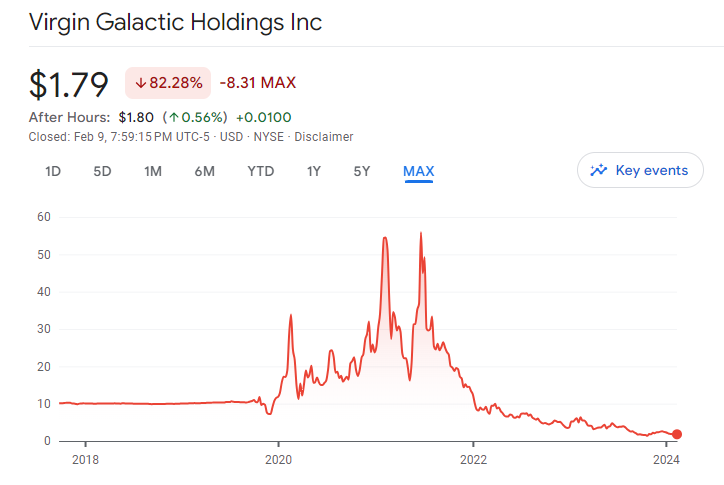
Special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) burst onto the scene in the late 2010s, promising a revolutionary path to public markets for private companies. These “blank check companies” captivated Wall Street with their speed, flexibility, and access to retail investors. But what caused this meteoric rise, and why did the SPAC party come to a screeching halt? This article delves deeper into the story of SPACs, exploring their initial allure, the factors behind their explosive popularity, and the forces that led to their dramatic fall from grace.
From Humble Beginnings to Wall Street Darling:
SPACs weren’t always the darlings of financial news. Existing since the 1990s, they remained relatively obscure investment vehicles until the perfect storm of low interest rates, abundant liquidity, and a yearning for innovation converged. Compared to the traditional IPO process, often perceived as sluggish and opaque, SPACs offered several advantages:
- Speed: Merging with a SPAC could take a private company public in months, compared to the 18-24 months of a traditional IPO. This faster route was particularly appealing to high-growth tech companies eager to access capital quickly.
- Flexibility: Unlike traditional IPOs with their rigid structures, SPACs offered more flexibility in deal terms and compensation, making them attractive to target companies.
- Retail Investor Access: Retail investors, typically excluded from pre-IPO rounds, could now participate in promising companies through SPACs, democratizing access to potentially high-growth investments.
The Intoxicating Frenzy: Celebrities, Hype, and Inflated Valuations:
Fueled by these advantages and a favorable market environment, SPACs experienced an unprecedented boom. The year 2020 saw a record-breaking number of SPAC IPOs, raising hundreds of billions of dollars. Celebrities like Shaquille O’Neal and Colin Kaepernick jumped on the bandwagon, launching their own SPACs and further amplifying the excitement. Media outlets buzzed with SPAC news, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy of investor enthusiasm and inflated valuations.
However, beneath the glitz and glamour, concerns simmered:
- Due Diligence Concerns: The compressed timeframe for finding a target company raised concerns about the thoroughness of due diligence, potentially leading to rushed and risky deals.
- Sponsor Compensation: The significant fees earned by SPAC sponsors, regardless of the target company’s performance, created potential conflicts of interest.
- Inflated Valuations: Many SPAC-backed companies lacked established revenue or profits, yet traded at sky-high valuations, raising concerns about a potential bubble.
The Sobering Reality Check: Bust, Scrutiny, and Uncertain Future:
The party couldn’t last forever. In 2021, the SPAC bubble burst due to several factors:
- Poor Performance: Many SPAC-backed companies underperformed, failing to live up to the lofty expectations set by their valuations. Investor disappointment mounted as promised returns failed to materialize.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: The SEC, concerned about potential conflicts of interest and disclosure issues, launched investigations and proposed new regulations, adding uncertainty to the SPAC landscape.
- Market Correction: Rising interest rates and a broader market sell-off dampened investor appetite for risky assets, further impacting SPACs.
SPACs Today: A Shaky Future or Niche Relevance?
SPAC activity has significantly declined, with many trading below their IPO price. The future of SPACs remains uncertain:
- Regulatory Landscape: New regulations could increase costs and complexities, making SPACs less attractive for sponsors and target companies.
- Investor Skepticism: Investors are more cautious, demanding stricter governance and clearer terms from SPACs before considering them as an investment vehicle.
- Niche Applications: While the broader SPAC landscape might remain subdued, SPACs could still find relevance in specific industries or situations where their flexibility and speed offer advantages.
Beyond the Boom and Bust: Lessons Learned:
The SPAC saga offers valuable lessons for investors, businesses, and regulators alike:
- High-risk, High-reward: SPACs offer faster routes to public markets, but come with inherent risks and require careful due diligence from both sponsors and investors.
- Regulation Matters: Clear and fair regulations are crucial for protecting investors, ensuring market stability, and fostering responsible innovation in the financial system.
- Innovation is Double-edged: Innovative financial instruments like SPACs require careful evaluation and responsible use to avoid unintended consequences and potential bubbles.
While the future of SPACs remains uncertain, their story serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of financial markets, the importance of informed decision-making, and the need for a balanced approach to innovation and regulation. It’s a cautionary tale for investors seeking high-risk, high-reward plays,
Persistent Liquidity: Despite the recent pullback, ample liquidity remains in the market, which could fuel future SPAC activity, particularly for well-structured deals with promising targets. SPACs could still offer advantages for companies seeking a faster, more flexible route to public markets compared to traditional IPOs.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape: The SEC’s proposed regulations, while adding some hurdles, could ultimately create a more stable and transparent SPAC market, potentially attracting more institutional investors wary of the earlier Wild West environment.
SPAC 2.0: Lessons Learned, Adaptations Made:
The SPAC industry is likely to adapt and evolve in response to the lessons learned from the boom and bust. We might see:
- Increased Focus on Quality: Sponsors and investors are likely to prioritize thorough due diligence, focusing on companies with proven track records and realistic valuations.
- Stronger Governance: SPAC structures could incorporate stricter governance provisions to address concerns about sponsor compensation and conflicts of interest.
- Niche Applications: SPACs might find success in specific industries like cleantech or healthcare, where their flexibility aligns well with the needs of emerging companies.
The Final Curtain or Act II?
Predicting the future of SPACs is tricky. While the frothy days of 2020 are unlikely to return, they remain a unique and potentially valuable tool in the financial landscape. Their ultimate fate will depend on several factors:
- The effectiveness of new regulations in striking a balance between fostering innovation and protecting investors.
- The ability of SPAC sponsors to adapt their strategies and regain investor trust.
- The overall health of the capital markets and investor appetite for riskier assets.
One thing is certain: the SPAC saga has been a dramatic and educational chapter in financial history. It serves as a reminder of the inherent risks and rewards associated with innovation, the importance of responsible regulation, and the ever-evolving nature of financial markets. Whether SPACs fade into obscurity or write a new chapter in their story remains to be seen, but the ride is far from over.
Beyond the Headlines: A Look at Specific Examples
To fully understand the nuances of the SPAC story, it’s helpful to delve into specific examples. Consider Virgin Galactic, whose meteoric rise and subsequent fall mirrored the broader SPAC narrative. Palihapitiya’s IPOC SPAC sent Virgin Galactic’s stock soaring in 2020, but it has since fallen significantly, highlighting the challenges of inflated valuations and the need for companies to deliver on their promises. Conversely, consider Latch, a home access solutions company that successfully merged with a SPAC in 2021. By focusing on a clear value proposition, strong execution, and responsible use of SPAC proceeds, Latch has navigated the challenging market environment and emerged as a potential success story.
Beyond Borders: The Global SPAC Stage
While the SPAC story has primarily unfolded in the US, it’s worth exploring its global reach. Europe and Asia are witnessing a growing interest in SPACs, with their own regulatory frameworks and unique dynamics:
- European Promise: Europe offers a potentially fertile ground for SPACs, with a fragmented tech landscape and a desire for alternative funding options. However, stricter regulations and different investor preferences may shape the European SPAC evolution differently than the US model.
- Asian Ambitions: SPACs are gaining traction in Asian markets like Singapore and Hong Kong, fueled by abundant liquidity and a focus on emerging tech sectors. Cultural nuances and regulatory approaches will likely influence the development of the Asian SPAC landscape.
Understanding the global context adds another layer of complexity and intrigue to the SPAC story. It highlights the potential for this instrument to adapt and evolve across different markets, catering to specific needs and regulations.
The Human Element: From Visionaries to Skeptics
The story of SPACs is not just about numbers and valuations; it’s also about the individuals who shaped its narrative. Key figures like Chamath Palihapitiya, the “SPAC King,” became synonymous with the boom, their bold pronouncements fueling both excitement and controversy. As the bubble burst, these figures faced criticism and scrutiny, raising questions about accountability and responsible leadership in the financial world.
On the other hand, many retail investors who participated in the SPAC frenzy now face losses, highlighting the importance of financial literacy and responsible investment practices. Their experiences serve as a cautionary tale for future generations navigating the ever-evolving world of finance.
The Final Act: A Legacy of Innovation and Lessons Learned
The SPAC saga offers valuable lessons for various stakeholders:
- Investors: Conduct thorough due diligence, understand the inherent risks, and avoid chasing hype over substance.
- Businesses: Prioritize responsible use of SPAC proceeds, focus on long-term value creation, and maintain transparency with investors.
- Regulators: Strike a balance between fostering innovation and protecting investors through well-designed regulations.
What is a SPAC?
A SPAC, or Special Purpose Acquisition Company, is a shell company with no actual business operations. It raises money through an IPO to acquire another, private company, making it public in the process. Think of it as a blank check company searching for a target to buy.
Why were they so popular?
SPACs offered several advantages:
- Speed: They could take companies public much faster than traditional IPOs.
- Flexibility: They offered more flexibility in deal terms and compensation, appealing to target companies.
- Retail investor access: Regular investors could participate in promising ventures earlier than usual.
What caused the SPAC bust?
Several factors contributed:
- Inflated valuations: Many SPAC-backed companies lacked proven track records yet traded at high valuations, raising bubble concerns.
- Poor performance: Many companies underperformed, failing to live up to expectations.
- Regulatory scrutiny: Concerns about potential abuses led to investigations and proposed regulations.
Are SPACs dead?
The future is uncertain. Regulatory changes, investor skepticism, and poor performance have dampened enthusiasm. However, they might still find niche applications in specific sectors where their flexibility remains valuable.
Should I invest in SPACs?
SPACs carry significant risks. Thorough due diligence, understanding the target company, and managing your expectations are crucial. Consult a financial advisor for personalized advice before investing.
